Oh this is a good one. Science + curiosity + clear numbers? That’s evergreen traffic if you structure it right.
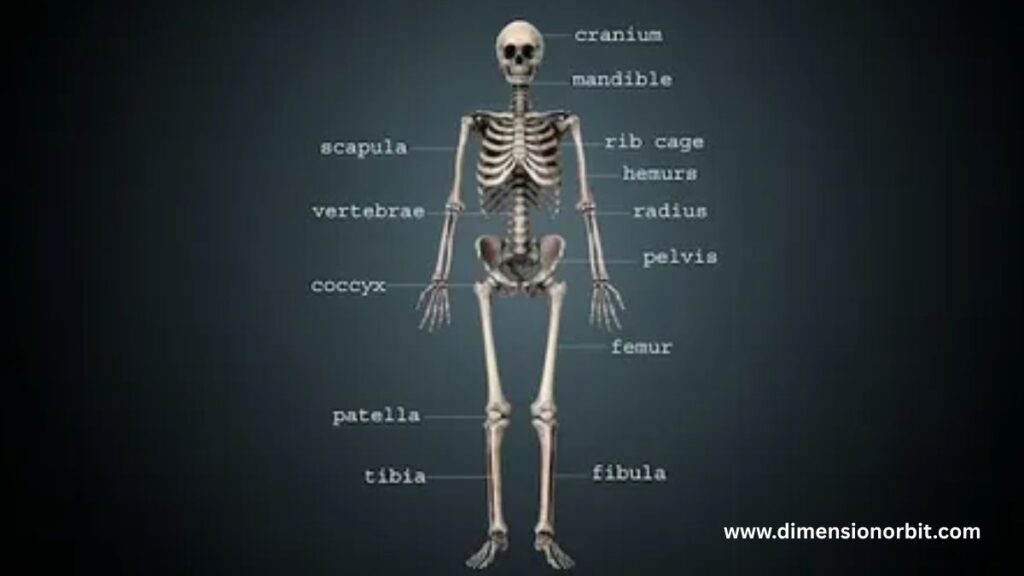
If you’ve ever wondered about the average weight of human skeleton, you’re not alone. It’s one of those questions that sounds simple but opens the door to fascinating anatomy, bone density science, and body composition analysis.
So, how much does a human skeleton weigh?
Short answer: about 15% of your total body weight.
But that number shifts depending on age, sex, height, genetics, and bone density. In this in depth guide, we’ll break down:
- Average male skeleton weight
- Average female skeleton weight
- Child skeleton weight
- Bone mass percentage
- Skeleton weight in pounds and kg
- How bone density changes over time
Let’s dig into the science.
What Is the Average Weight of a Human Skeleton?
The average weight of a human skeleton in a healthy adult ranges between:
- 9–11 kg (20–24 pounds) for men
- 7–9 kg (15–20 pounds) for women
That represents roughly 12–15% of total body weight.
Here’s the key formula:
Skeleton weight ≈ 14–15% of total body weight
For example:
- A 180 lb (82 kg) adult male → Skeleton weighs ~25 lb (11 kg)
- A 140 lb (63 kg) adult female → Skeleton weighs ~20 lb (9 kg)
That percentage accounts for bone mineral content, water inside bone tissue, and marrow weight.
Skeleton Weight Percentage of Body Weight
Your bones are surprisingly heavy. They form the structural framework of your body, and they’re made of dense, mineralized tissue.
Here’s a breakdown:
| Body Weight | Approximate Skeleton Weight | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 120 lbs | 16–18 lbs | 13–15% |
| 150 lbs | 20–22 lbs | 14–15% |
| 180 lbs | 24–27 lbs | 14–15% |
| 200 lbs | 28–30 lbs | 14–15% |
The skeleton weight percentage of body weight stays fairly consistent across adults, assuming healthy bone density.
Bob Kelly Height, Bio, Age, Wife, Family
Average Male Skeleton Weight
The average male skeleton weight tends to be heavier due to:
- Larger frame size
- Higher bone mineral density
- Greater mechanical load from muscle mass
Typical numbers:
- Adult male skeleton weight: 9–11 kg
- Skeleton weight in pounds: 20–24 lbs
- Bone mass percentage: ~15%
Men generally reach peak bone mass around age 25–30.
After that, gradual bone loss begins unless maintained through resistance training and proper nutrition.
Average Female Skeleton Weight
The average female skeleton weight is slightly lower.
Typical numbers:
- Adult female skeleton weight: 7–9 kg
- Skeleton weight in pounds: 15–20 lbs
- Bone mass percentage: 12–14%
Hormonal differences, particularly estrogen levels, influence bone density in women. After menopause, bone loss accelerates due to hormonal shifts.
This is why osteoporosis risk is higher in women.
How Much Does a Child’s Skeleton Weigh?
A child’s skeleton is lighter and less dense because bones are still developing.
At birth:
- Infants have around 270 bones
- Many are soft cartilage
- Average skeletal weight: ~350–500 grams (0.8–1.1 lbs)
By adolescence:
- Bones fuse into the standard 206 adult bones
- Bone density increases significantly
Estimated skeleton weight by age:
| Age | Approximate Skeleton Weight |
|---|---|
| 5 years | 2–3 kg (4–6 lbs) |
| 10 years | 4–6 kg (9–13 lbs) |
| 15 years | 6–9 kg (13–20 lbs) |
Bone growth stages peak during puberty due to hormonal surges.
Heather Holmes Height, Bio, FOX News Career, Age
Bone Composition: Why Bones Are Heavier Than They Look
Your skeleton isn’t hollow like a Halloween prop. It’s dense and complex.
Bones are made of:
- Cortical bone (compact bone) – outer layer, dense and strong
- Trabecular bone (spongy bone) – inner layer, porous but sturdy
- Calcium and phosphate minerals
- Collagen fibers
- Bone marrow
Approximately:
- 65% mineral content
- 25% organic matrix
- 10% water
This mineralization explains why the weight of human bones is substantial despite their appearance.
Compact Bone vs Spongy Bone
Not all bone tissue weighs the same.
Compact bone (cortical bone):
- Dense
- Found in long bones
- Supports weight-bearing
- Heavier per volume
Spongy bone (trabecular bone):
- Porous
- Found inside vertebrae and pelvis
- Lighter but strong under compression
This balance allows bones to remain strong without becoming too heavy.
Do Taller People Have Heavier Skeletons?
Yes, generally.
Taller individuals have:
- Longer bones
- Greater skeletal surface area
- Higher skeletal mass
However, height alone doesn’t determine bone weight. Genetics and frame size matter more.
Two people of equal height may have different skeletal mass due to bone mineral density and build.
Bone Density and DEXA Scan Measurements
If you want a precise measurement of your skeletal mass, doctors use a DEXA scan (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry).
DEXA scans measure:
- Bone mineral density
- Bone mineral content
- Total skeletal mass
- Body composition analysis
Athletes and medical patients use DEXA scans to monitor bone health.
Brian Brenberg Height, Bio, FOX Business, Age, Family,Net Worth
How Bone Density Changes Over Time
Peak bone mass occurs between ages 25–30.
After 30:
- Bone remodeling slows
- Bone loss begins gradually
- Women may lose 1–2% per year after menopause
By age 70:
- Up to 20–30% of bone mass may be lost without intervention
This directly affects human skeleton weight in older adults.
Factors That Affect Skeleton Weight
Several variables influence skeletal mass:
- Age
- Sex
- Genetics
- Nutrition (calcium & vitamin D)
- Hormonal levels
- Weight-bearing exercise
- Chronic illness
- Osteoporosis or osteopenia
Weight-bearing exercise increases bone density by applying mechanical load on bones.
Is Bone Heavier Than Muscle?
Pound for pound, bone tissue is denser than muscle tissue.
However:
- You have far more muscle mass than bone mass.
- Muscle makes up 30–50% of body weight.
- Bone makes up around 15%.
So bones are denser, but muscles contribute more total weight.
Do Athletes Have Heavier Skeletons?
Yes.
Athletes who engage in:
- Weightlifting
- Sprinting
- Gymnastics
- Contact sports
often develop increased bone mineral density.
Mechanical stress stimulates bone remodeling, making bones stronger and slightly heavier.
This is especially true in long term resistance training.
Scientific Breakdown of Bone Mass
Here’s how body mass distributes in an average adult:
| Body Component | Percentage of Total Weight |
|---|---|
| Muscle | 30–50% |
| Fat | 10–30% |
| Bone | 12–15% |
| Organs | 10–15% |
| Water | Variable |
This demonstrates that skeletal mass in body composition plays a significant structural role.
Fun Facts About the Human Skeleton
- Adults have 206 bones
- The femur is the strongest bone
- The stapes (in the ear) is the smallest bone
- Bones are 5 times stronger than steel by weight
- Bone is living tissue and constantly remodels
Digital tool
Digital tools like Feet and Inches Calculator can convert inches to centimeters or feet instantly. Many smartphone apps now offer augmented reality measuring features, allowing you to gauge objects virtually and compare them to known lengths.
FAQs
What is the average weight of a human skeleton?
Approximately 9–11 kg (20–24 lbs) for men and 7–9 kg (15–20 lbs) for women.
How much does a female skeleton weigh?
Around 7–9 kg or 15–20 pounds.
How much does a male skeleton weigh?
Around 9–11 kg or 20–24 pounds.
How much of body weight is bone?
Typically 12–15% of total body weight.
Does skeleton weight change with age?
Yes. It increases during growth and declines gradually after 30.
Do taller people have heavier bones?
Generally yes, though density and genetics matter more.
Is bone heavier than muscle?
Bone is denser per volume, but total muscle mass weighs more overall.
How much does a child’s skeleton weigh?
Between 2–9 kg depending on age and development stage.
Final Thoughts
The average weight of human skeleton may sound like a simple trivia question, but it actually reveals a lot about how your body works. On average, your bones make up about 12–15% of your total body weight, translating to roughly 15–25 pounds (7–11 kg) in most adults. That’s a significant portion of your body mass dedicated purely to structure and protection.
Your skeleton isn’t static. It constantly remodels, strengthens under mechanical load, and adapts to age, nutrition, and activity levels. Bone density peaks in early adulthood, then gradually declines without proper care.
So the real takeaway isn’t just how much your skeleton weighs. It’s this: strong bones are built over time, and you have more control over your skeletal health than you might think.

Jhon AJS, the author of Dimension Orbit, is an experienced blogger fascinated by the mysteries of existence. He explores every type of dimension from scientific to spiritual with clarity and creativity. Jhon’s engaging writing style invites readers to think deeper, question reality, and discover new perspectives on the universe.